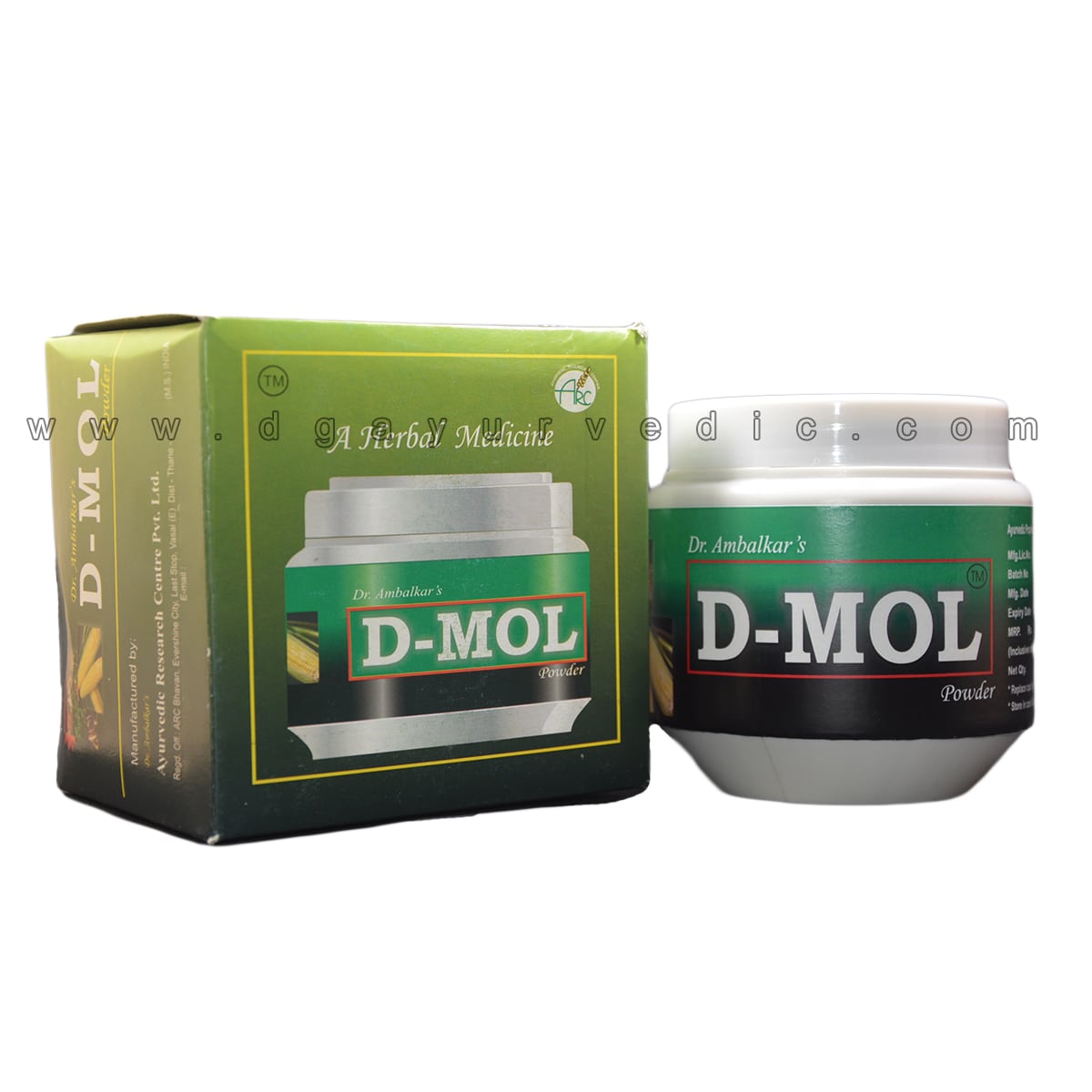
Dr. Ambalkars D-MOL Powder (Diabetes Care) 250 Grams
₹399
Description
Dr. Ambalkar’s D-MOL Powder 250 gms (Diabetes Care)
A Herbal Solution for Diabetes
- D-Mol is a well balanced combination of herbs, which increases glucose utilization in tissues and reduces the glucose level in the blood.
- It also regenerates the pancreatic cells to restore the function of Pancreas. By taking all the dietary precautions, D-MOL helps to regulate the blood glucose level within normal limit.
- Generally control over sugar level by D-MOL is expected within 3 to 4 months. (Results may vary).
Instructions to use D-MOL:
Dosage: Add 5 gms of D-Mol powder in a glass of boiled water and deep over night. Next morning, stir the mixture & drink it on empty stomach
1. Start D-Mol along with current treatment which patient is already taking for diabetes (For e.g. tablets, Insulin Injections, etc.)
2. Monitor the blood sugar level every month (or as frequently as required in case of patients on insulin).
3. Requirement of your present medicines will decrease slowly. Consult your family doctor for adjustment of their dosage (or change in medicine may require for patients on insulin).
4. After some period these medicines will not be required and only D-Mol with some dietary restrictions will control your sugar level very safely and smoothly as there is no risk of hypoglycemia (sudden lowering of blood sugar).
| Each 100 gms contains: | ||
| Latin Names | Hindi Names | Gms |
| Holarrhena antidysenterica | Kutaja | 07 g |
| Aegle marmelos | Bel Phal | 05 g |
| Trigonella foenumgraecum | Methi | 10 g |
| Eugenia jambolana | Jamun | 12 g |
| Swertia chirata | Chirayata | 07 g |
| Momordica charantia | Karela | 10 g |
| Hibiscus rosa-sinensis | Gurhal / Jaswand | 14 g |
| Terminalia citrina | Asan | 07 g |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra | Jethimadhu | 10 g |
| Pueraria Tuberosa | VidariKanda | 10 g |
| Emblica officinalis | Amla | 4 g |
| Terminalia bellirica | Baheda | 4 g |
| Sodium Benzoate (Preservative) | 0.5% | |
Net Content:
- D-MOL Powder One Jar – 250 gms
- Instruction Book
- Measuring Spoon
Dietary Restrictions
Don’ts
- Rice, Potato, Sweet Potato.
- Sugar, Honey, Sweets, Jaggery (Raw-Sugar)
- Bananas, Dates, Miserly (Chickoo), Grapes.
- Fried items like Vada, Samosa, Papad etc.
- Cold Drinks, Alcoholic Drinks, Smoking and Chewing of Tobacco.
Do’s.
- All cereals like Wheat, Jowar, Bajari etc.
- All Pulses.
- All vegetables & Salad.
- Onion, Garlic, Ginger & all spices.
- Fruits: Daily one or two except mentioned above.
- Non-Vegetarian food (only boiled not fried)
- Oil: Sunflower, Safflower or Corn Oil (Not to Fry)
- Oil seeds like sesame, lentil, Groundnut, Coconut (in less amount)
- Ghee (in less amount)
- Salt (as usual)
- However calories requirement for each and every patient depends on his or her lifestyle, dietary and exercise.
- Diabetic diet should be free from sugar and excess fats so as to maintain blood sugar instead of heavy lunch and dinner take small quantity of food for four and five times per day.
Replace cap tightly after use.
Store in cool & dry place.
General Information:
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus (generally known as DIABETES) is a clinical syndrome characterised by many harmful effects caused by excessive amount of glucose in the blood due to direct (type I) or indirect (type II) deficiency of Insulin in the human body.
- Insulin is the hormone secreted by “Pancreas” a gland that is situated in the abdomen of human body.
- This is the only anabolic hormone, which has profound effect on the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, & proteins which are present in the diet and absorbed in the body through intestines.
- In presence of insulin there is perfect balance between breakdown (Catabolism) and synthesis (anabolism) of glucose, which is tightly regulated by special mechanisms, and its level is maintained with in a narrow range of 3.5 to 6.5 m. mol / liter.
- Entry of glucose in the circulation is either from intestinal absorption after food intake or formation of glucose from liver.
- Glucose is transported and taken by the peripheral tissues like muscles for their activity.
- A steady supply of glucose is essential for the brain, which uses it as its principal fuel.
- When intestinal glucose entry declines in between food intakes, stored glucose is delivered from liver for routine activity.
- When there is deficiency of insulin in the body or decreased sensitivity to insulin, this balance is not maintained and amount of glucose in the blood starts increasing and its harmful effects starts appearing in the body.
- Thus, Glucose, which is the Lifesaver of the body, becomes the Killer, when present in excess amount.
Types of Diabetes:
Type I: Insulin dependent Diabetes:
Direct deficiency of insulin due to production failure in the pancreas.
Age at onset – Generally type I diabetes present in the patients with the age group less than 40 years.
Type II: Non Insulin dependent Diabetes:
Indirect deficiency of insulin either due to abnormal insulin or insulin resistance of tissues in the body.
Age at onset – Generally type I diabetes present in the patients with the age group more than 40 years.
Causes of Diabetes:
- In most of the cases of diabetes, precise cause is not known.
- Genetic factors – some genetic factors like HLA linked genetic predisposition are responsible.
- Environmental factors – like lifestyle, lack of exercise, dietary habits, stress, viral infections of insulin production mechanisms, etc.
Any of the above factors or their combined mechanisms can cause diabetes.
Symptoms of diabetes:
- Poly-urea (Frequent urination), poly dipsia (Frequent thirst), nocturia (frequent urination during night).
- More severe cases may present with rapid weight loss, Loss of skin turgor (texture). Sweet acetone smell of breath, Obesity, Chronic fatigue (early tiredness).
- Giddiness, painful and weakness of legs, repeated skin sepsis (boils), frequent of genital tract.
- Sometimes, patients may not show symptoms related to diabetes due to its early or late complications like food ulcerations, non healing wounds, cataracts in the eyes, Retinopathies and peripheral Neuropathies.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is done by investigations like random blood glucose level, fasting blood glucose, post – lunch blood glucose, glucose tolerance test & urine sugar levels. If blood glucose levels are not monitored and perfect control of these levels are not maintained diabetes can cause serious complications all over the body and therefore it is also called as Silent Killer Disease.
-
Complications:
1. Hypoglycemia:
- Sudden decrease in the blood glucose level is called as Hypoglycemia.
- This may occur due to untimely, improper and inadequate food intake of diabetic patient unexpected or unusual exercise Alcohol intake High doses of anti – diabetic drugs (improper management of doses)
2. Diabetic Keto acidosis
If treatment of Diabetes is inadequate, blood glucose level may become very high which can lead to unconsciousness.
3. Atherosclerosis
Thickening of blood vessel walls .
4. Retinopathy
These are the series of changes in the eyes due to uncontrolled diabetes, which can cause blindness.
5. Peripheral Neuropathy
These are the degenerative changes in the Peripheral nerves of the body which can cause:
i. Postural hypo tension.
ii. Constipation.
iii. Excessive Sweating.
iv. Impotence (due to neural damage)
v. Sepsis, abscess, non healing ulcer, gangrene etc.
Treatment of Diabetes:
- Type I – Due to absolute deficiency of insulin these patients are to be kept on insulin to control the diabetes.
- Type II – Many anti diabetic oral drugs are available to increase the sensitivity of insulin to target tissues. Insulin can be given along with these drugs, if required.
- Dietary restrictions are necessary along with the drug treatment of diabetes. Strict monitoring is necessary during the treatment to achieve the perfect control over blood glucose level and to prevent serious complications of diabetes.
Problems related with above treatment:
1. Gradual decrease in the potency of the drugs to maintain the glucose level and to use new drugs or different drug combinations.
2. Frequent changes of the drugs is necessary with monitoring of the blood glucose level to avoid side effects.
3. Irregular intake of medicines and non – compliance of dietary restrictions by patients may require insulin therapy.
4. Patients have to undergo frequent investigations regarding glucose levels and strict vigilance over early complications.
5. Patients are dis comfortable with the insulin injections and their frequency of administration. It is to be noted that by getting patients compliance and consistency the above problems can be overcome. After all, there is no cure for diabetes and only life long control is possible in modern medicine.
After Reviewing the problem of diabetes and its available treatments in modern medicines, Ayurvedic Research Center (ARC) has made a research for Ayurvedic medicine and after a series of trials, has successfully launched the Ayurvedic Medicine ‘D-MOL.
Additional information
| Weight | 350 g |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 1 × 1 × 1 cm |
Brand
Dr. Ambalkar's
3 reviews for Dr. Ambalkars D-MOL Powder (Diabetes Care) 250 Grams
You must be logged in to post a review.










S K Sangam (verified owner) –
Dattakumar (verified owner) –
Good service and timely delivery
Anonymous (verified owner) –
All good